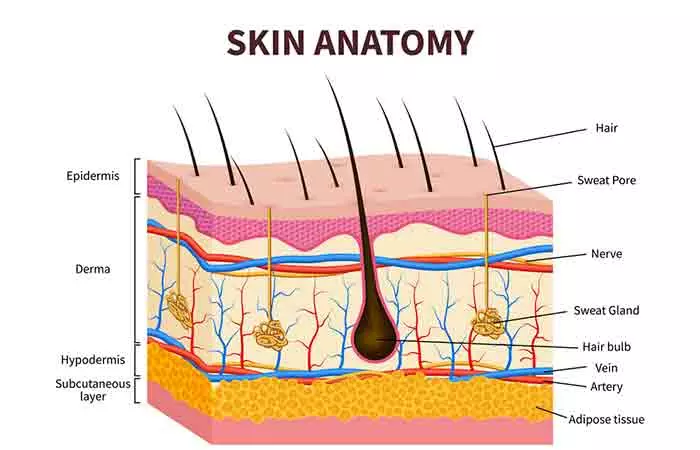
What Is Thin Skin?
Thin skin has a leaner epidermis (top layer) and lacks the stratum lucidum layer. The epidermis has a total of five layers (1):
Stratum basale or Stratum germinativum: It is the deepest layer of the epidermis and contains melanocytes (cells that produce melanini A natural substance produced by the body that helps provide pigmentation to the skin, hair, and eyes. ). Stratum spinosum: It has 8-10 cells layers and contains the dendritic cells (a type of immune cells). Stratum granulosum: It has 3-5 cell layers and contains the glycolipids that keep the skin cells stuck. Stratum lucidum: It contains 2-3 cell layers and is only found in thick skin in the soles and palms. Stratum corneum: It is the uppermost skin layer and has 20-30 cell layers made of keratini A fibrous protein found in the body that helps structure nails, hair, and the outermost layer of the skin. and dead keratinocytes (cells that produce keratin).
Now, let’s understand what thick skin is. The upper back skin is the thickest (considering the thickness of the dermis) but is considered thin skin as it has a thinner epidermis.
What Is Thick Skin?
Unlike thin skin, thick skin has all five epidermis layers and is mainly present in areas that receive the most friction, like the fingertips, palms, and soles. Thick skin is hairless and does not contain sebaceous glands and apocrine sweat glands as it opens in the hair follicle. This graph from a study published in the Journal of Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials shows the thickness of the skin around the body. The stratum corneum (SC) of the heels increased in thickness with overextension, from 267 m to 316 m (p = 0.02). In both types of postures (relaxed and overextended), the thickness of load-bearing sites (mean 315 m), such as the foot, fingertip, and heel was significantly (p 0.01) higher than the thickness of non-load-bearing sites.
Thickness Of Stratum Corneum
While the skin is naturally thicker or thinner on different body parts, various other factors may also cause someone to have thick or thin skin. Let’s understand in the next sections.
Causes Of Thin Skin
Our skin naturally becomes thinner with age. This happens due to a decrease in elastin and collagen production (2). Taking certain medications, particularly steroids, may lead to skin thinning as a side effect.
Causes Of Thick Skin
Some people may naturally have thicker skin due to genetics. Skin conditions like calluses or corns may result in thickened skin on the feet or hands, due to repeated friction or pressure. Underlying medical conditions like diabetes may also affect skin thickness (3). Skin conditions like psoriasis or eczema may also lead to thickened skin patches (4),(5).
If you’re concerned about the thinning or thickening of your skin, consult a healthcare professional to determine the cause and explore potential treatments. Here is a brief overview and comparison between the structure of thin and thick skin.
Thick Skin Vs. Thin Skin
Thin skin contains:
Hair follicles connected to different glands and muscles help to regulate body temperature and repair wounds (6). Sebaceous glands produce sebum to keep the skin nourished, moisturized, and protected. Sweat glands regulate body temperature.
Thick skin:
Prevents damage to areas that are exposed to maximum friction. Has eccrine sweat glands that help regulate body temperature.
In A Nutshell
Does skin thicken with age? No, the outer layer of the skin tends to get thinner with age (7). Is thick skin genetic? Yes, thick skin could be seen in certain skin conditions that are a result of genetic mutations (8). What is the best vitamin for the skin? Vitamins D, A, C, and E are all essential for developing and maintaining a healthy skin barrier (9). Is milk good for skin? Yes, milk is rich in proteins and is known to have antibacterial and antioxidanti A substance that fights the ill effects of free radicals in the body, thereby protecting the skin from damage and improving its texture. properties that can help heal and restore your natural skin barrier (10).
Illustration: Thin Vs. Thick Skin: Definitions Differences And Similarities
Unravel the intriguing world of thick and thin skin in this eye-opening video. Click on it to delve into the science behind these contrasting types and understand how they impact our daily lives.