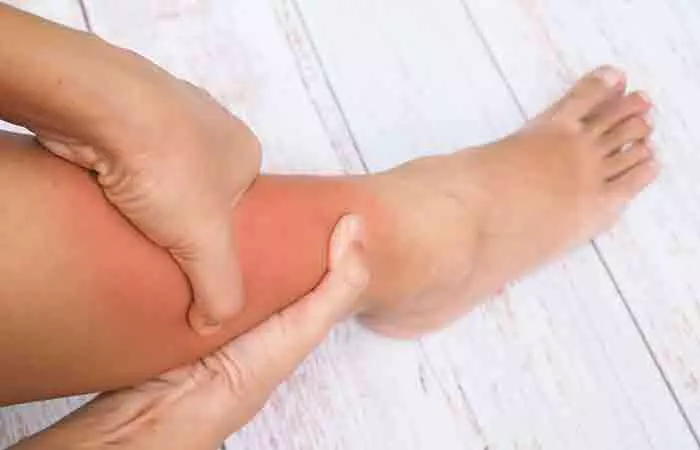
Bleeding. Burning sensation around the wound. Painful swelling. Skin redness. Pus discharge. Bruising. Muscle pain. Difficulty moving the limb. Limping or an inability to walk (if it is not your leg). Pain that spreads to the area surrounding the avulsion.
What Causes Skin Avulsion?
A variety of events can cause skin trauma like avulsion. These include:
Explosions Accidents Gunshots Animal bites Industrial equipment injuries
How To Treat Skin Avulsion
Skin avulsion can be treated by following a few home care tips and taking certain medications.
Home Care
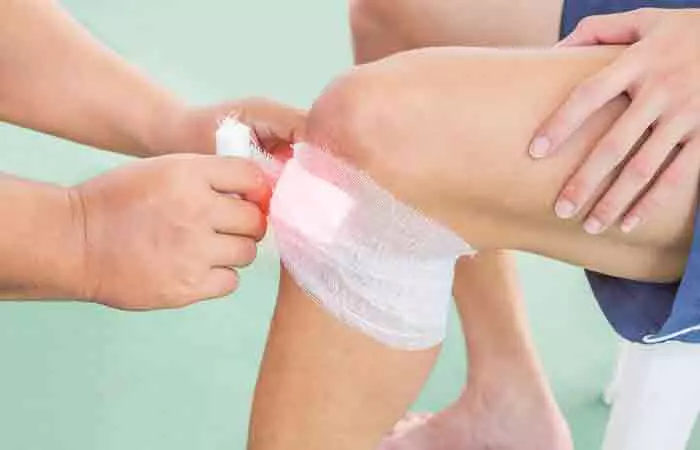
Wash the wound and disinfect it and remove unwanted dirt and debris. Apply pressure and elevate the wound to stop the bleeding. Wrap a clean bandage around the wound. Keep the wound and bandage clean and dry for at least a week. Also, make sure you get adequate nutrition and relaxation for faster healing.
Some minor abrasions can be treated at home without the need for a doctor. Seek medical help if the damage is significant. Melissa Jones, a blogger, wrote about her first-ever skin avulsion and how she got another one later in life. She had a nail skin avulsion when she lost a big toenail while moving a desk in school. The recent skin avulsion occurred when she cut her left index fingernail. She bound up the wound and went to the ER. When the wound was opened for examination 2 hours later, it was still bleeding. She wrote, “Thankfully the doctor had just the right knowledge and tools to treat the nail avulsion. I now have a fingernail made of surgifoam to protect the nail bed while it heals, and a ready supply of gauze to protect it even further (i).” This descriptive prevalence study analyzed data from nursing facilities over 5 years comprising 188,675 cases of skin tears in patients 20 years and older. The median healing time was observed to be 15 to 27 days, and 10.3–12.8% of the skin tears increased in frequency with age.
Medications
People may take over-the-counter (OTC) medications during the healing phase to minimize inflammation and uncomfortable symptoms. Avoid Aspirin as it may induce bleeding and slow down the healing process. In case of lacerations, severe or infected wounds, a healthcare provider may prescribe stronger pain medication. Topical antibiotics can be used for small cuts and scrapes. However, if the wound is at a high risk of developing an infection, a healthcare provider may prescribe oral antibiotics. Dr. Daniel Boyer, M.D., author at Farr Institute, suggests the following steps to treat a skin avulsion:
Allow the skin to heal on its own. Get the edges of the wound stitched together if the wound is small. The doctor may reattach the avulsed skin and graft skin over the wound.
Not all skin avulsions can be treated at home. Some of them need immediate medical attention. Keep scrolling to learn when to see a doctor.
When To Seek Medical Advice
Call your healthcare provider right away if any of these occur:
The wound pain increases, or you develop new pain. You notice redness, swelling, or pus on the wound. You develop a high fever. You have trouble moving the injured area. The sutures come apart before your next appointment. The wound edges look as if they will re-open. The wound splits open or does not heal. Uncontrolled bleeding. The wound becomes infected.
Board-certified dermatologist and medical advisor Dr. Jen Haley adds, “If you suffer from a major skin avulsion, you should seek medical treatment immediately to prevent any further damage to your skin. Avulsion injuries almost always require medical care, and you will need to be assessed to see if you need surgical intervention.” It is important to be aware of the difference between avulsion and abrasion so you can get the right treatment immediately.
Skin Avulsion Vs. Abrasion
Abrasion and avulsion are both skin injuries, but they differ in significant ways. An abrasion is a superficial wound where the top layer of skin is scraped off due to friction or contact with a rough surface. It can be categorized from mild to severe. While mild abrasion, like minor scratches, can be treated with first-aid, a severe one, where tissues and skin are wounded from continual pressure from an object, requires immediate medical attention. Mild abrasion usually doesn’t leave a scar, meanwhile, severe ones might. Avulsion, whether mild or severe, requires immediate medical attention or it might get infected and leave a scar. How long does avulsion take to heal? Avulsion may take three to twelve weeks to heal completely. Does an avulsion need stitches? Avulsions cannot be stitched as there will be tissue damage. However, medicinal compliance and proper care may fasten healing. Is a skin avulsion the same as a skin tear? Yes, skin tears are medically referred to as skin avulsions. What is the difference between avulsion and laceration? In a skin avulsion, the top layer of the skin peels or tears off due to an injury. In case of laceration, the skin or body tissue split open from being hit by a blunt force. How can I prevent scarring or other cosmetic damage as my skin avulsion heals? You can learn how to prevent scarring after a skin avulsion by keeping the wound clean and moist. Keep the wound clean and dress it with an ointment and bandage to minimize the chances of scarring.
Illustration: Skin Avulsion: Symptoms Causes And Treatments
Learn about the different types of open wounds: abrasions, lacerations, skin avulsions, and punctured wounds. And understand how to identify and treat each type of wound with the video below.