Tortillas, raw and dressed corn cobs, nachos, or even cornmeal – this veggie tastes heavenly in any form. Corn not only tastes great but also offers many health benefits. It can effectively manage many ailments. Did you know that it can promote hair growth and effectively combat inflammation? Learn more about the health benefits offered by this bright veggie by reading the article below. Keep scrolling!
Corn: An In-depth Insight
This graph represents the global import value of corn in 2021 by country. China is in the lead (8.02 billion US dollars), followed by Mexico in second place (5.12 billion US dollars), and Japan in third place (4.74 billion US dollars). What Are Its Benefits? Its antioxidant content may fight diabetes, boost iron levels, and aid in weight loss. Who Can Consume It? Anyone who is not allergic to corn can consume it. How Often? You can consume it daily but in moderation. Caution Overconsumption of corn can cause digestive problems.
Major Corn Importers Of The World
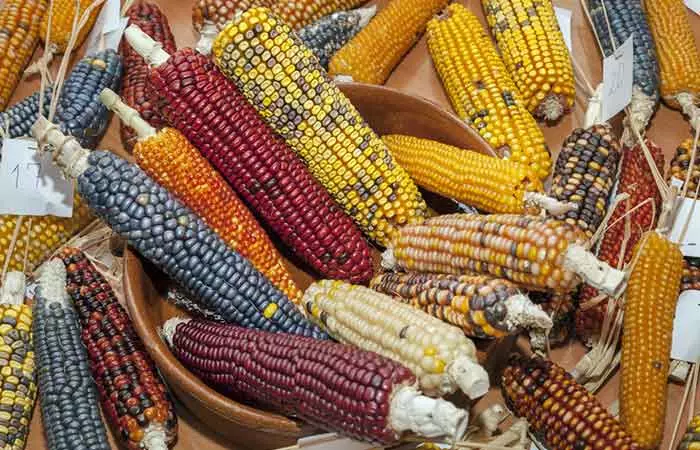
Corn (Zea mays) is the edible grain (seed) of the cereal plant belonging to the grass family (Poaceae). This domesticated crop originated in the Americas and is one of the most widely distributed food crops in the world. Corn is used as livestock feed, human food, biofuel, and raw material in several industries. The most popular varieties for consumption are yellow and white corn. There are also varieties of corn with red, blue, pink, and black kernels that are often banded, spotted, or striped. That’s the result of some incredible genetic interplay!
Types Of Corn
Dent Corn: Has a depression in the crown of the kernel that is caused by unequal drying of the hard and soft starch making up the kernel. Flint Corn: Contains a little soft starch and has no depression. Flour Corn: Largely made up of soft starch and has soft, mealy, easily ground kernels. Sweet Corn: Has wrinkled translucent seeds. The plant sugar is not converted to starch as in other types, thus imparting it sweetness. Popcorn: An extreme type of flint corn that is characterized by small, hard kernels devoid of soft starch. Heating it causes the moisture in the cells to expand, making the kernels explode. Corn is not only composed of starch but is also loaded with fiber, carbs, mineral, vitamins, and other micronutrients. Check out the next section for its nutritional value.
Nutrition Profile Of Corn
Yellow corn is the most commonly used variety of corn. White corn has the same nutritional value, with one exception – yellow corn has more fiber than the white variety. Corn has an interesting phytochemical profile too. Among cereals, corn has one of the highest levels of phenolic compounds. This means it has excellent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer properties. Corn also has cancer prevention properties, which can help in reducing the risk of getting cancer. Anthocyanins, coumarins, trihydroxybenzoic acid, vanillic acid, caffeic acid, ferulic acid, chlorogenic acid, hydroxyphenyl acetic acid are present in corn. Also, flavonoids like quercetin, rutin, hirsutrin, morin, kaempferol, naringenin, hesperitin, zeaxanthin, lutein, and their derivatives are commonly seen in this cereal (1). Since corn is a treasure chest of phytochemicals, eating it will give you a total health makeover. The antioxidants present in corn help cure a broad spectrum of diseases. Want to know which ones? Alright, then! Brace yourselves for a healthy dose of science and evidence.
What Are The Benefits Of Eating Corn?
1. Controls Diabetes
Corn helps in diabetes management. Hyperglycemia (increased blood glucose levels) results in hypoxia (low oxygen level in blood). Hypoxia gets aggravated when there are free radicals in your blood. Corn also helps to aid blood pressure and promote heart health. These free radicals or reactive oxygen species trigger inflammation of tissues and undesired proliferation of cells. The anthocyanins and flavonoids present in corn are potent free radical scavengers. They eliminate free radicals, improve blood flow, protect pancreatic β-cells, increase insulin secretion and sensitivity, and prevent renal failure (2), (3). In addition, the hair or silk of sweet corn may help treat diabetes. Suituapui, a blogger, explained how her late father treated his diabetes with sweet corn silk. She writes, “It was good for treating diabetes, so he went round collecting all that he could find and dried them in the sun. He would boil it to make tea and drink and eventually, he managed to get everything under control (i).” This highlights one of the lesser-known sweet corn benefits, especially for those managing diabetes naturally.
2. Might Aid Weight Loss
Corn silk – which is the stigma of maize – is a soft, thread-like waste material that is either green or yellow. There are notable corn silk benefits as it contains many essential flavonoids, tannins, saponins, alkaloids, and sitosterol, along with calcium, potassium, and magnesium. These phytochemicals in corn silk regulate the genes that control fat accumulation, fat cell (adipocytes) differentiation while increasing the rate of lipolysisi A metabolic process that breaks down fat cells in the body to reduce the volume of fatty tissue and tightens the skin. , and fatty acid metabolism. This can potentially help you lose weight (4). However, many papers have demonstrated the role of corn and its starch in weight gain and obesity (5).
3. Could Reduce Inflammation
Inflammation is your body’s way of responding to threats like pathogens, free radicals, heavy metals, toxic intermediates, overdose, deficiency, external stimuli, and any other unfavorable physiological stress. The proteins and phytochemicals present in different part of maize offer protection to your body from such pro-inflammatory agents. Corn gluten is one such protein. Flavonoids like quercetin, naringenin, and lutein, along with anthocyanins, also inhibit the activation of several pro-inflammatory genes and cellular mechanisms (6), (7). As per this theory, a corn-rich diet can reduce constipation, asthma, arthritis, irritable bowel disease, GERD, and dermatitis. However, there is extensive evidence out there that shows corn is a pro-inflammatory agent. Blame the starch and fats!
4. Boosts Iron levels
Anemia develops as a result of iron deficiency in your body. A fall in hemoglobin levels leads to several developmental issues. Anemic children have stunted growth, retarded cognitive and psychomotor development, and weak/underdeveloped immune system. Iron plays a vital role in oxygen and nutrient transport, energy metabolism, and menstruation. You must have noticed in the nutritional profile of corn that it contains iron in abundance. Adding maize or corn derivatives to your diet in required amounts can solve issues related to anemia, particularly in children and women. Having optimum iron in your body is also essential for the health of your eyes, hair, and skin health (8).
5. Enhances Endurance And Physique
All scientists agree that carbohydrates are the best fuel for your body during prolonged exercise. Our hero – corn – oozes carbs. What’s even better is that corn has a moderate glycemic index of about 56 to 69. The fiber and carbs present in corn help in building your dream body. Though the digestion process of carbohydrates is quicker compared to that of protein or fat, they can be stored in your cells for a long time without triggering inflammation. Therefore, corn is the solution, especially for athletes and regular heavy-duty gymmers (9).
6. Improves Vision
Lutein and zeaxanthin are two carotenoidsi Naturally occurring pigments in plants that are rich in antioxidants and enhance immunity and vision. that play an important role in vision development. Deficiency of these carotenoids causes cataract, macular degenerationi An eye disease that causes the macula (the central section of the retina) to deteriorate and lead to loss of vision. , and age-related ophthalmologic disorders. Corn contains 21.9 μgg of lutein and 10.3 μg/g of zeaxanthin, along with ß-cryptoxanthin and ß-carotene, which promotes eye health. When white, yellow, high-carotenoid, blue and red corns were tested for their lutein content, it was found to be the highest in yellow corn (406 µg/100 g) and lowest in blue and white corns (5.2 and 5.7 µg/100 g, respectively) (10). Want to get rid of those thick spectacles? Binge on some fresh corn. What’s the best way to have corn? By adding it to your daily diet, of course. I’ve collected some simple, quick, and healthy recipes with corn for you. Let’s see how they turn out!
Healthy Recipes With Corn
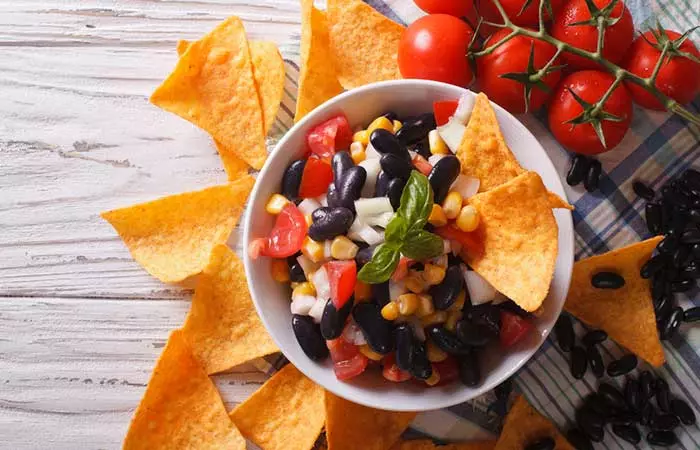
1. Tangy Corn Salsa
Corn on the cob: 4 ears, with husk Black beans: 2 cans (15 oz.), unsalted, drained, and rinsed Plum tomatoes: 6, chopped Green bell pepper: 1, chopped Red onion: 1, diced Jalapeno peppers: 2, chopped Lime juice: 1 lime (equivalent) Cilantro: 2 teaspoons, freshly chopped Garlic: 2 cloves, minced Tomato juice: 14 oz. Tomato sauce: 14 oz. Kosher salt: 1 pinch or to taste Black pepper: 1 pinch, ground, or to taste
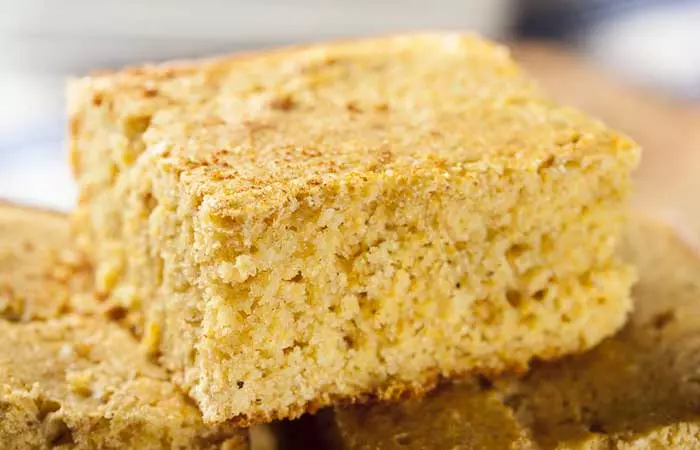
2. Quick-n-Creamy Corn Cake
Butter: ½ cup, melted Eggs: 2, beaten Dry cornbread mix: 1 packet (8.5 oz) Whole kernel corn: 1 can (15 oz), drained Creamed corn: 1 can (14.75 oz) Sour cream: 1 cup
Once you taste these dishes, you will not want to stop cooking and experimenting with corn. Corn is one of the tastiest additions to any dish.
Does Corn Have Any Side Effects?
Yes, it does! The high starch, fatty acids, and linoleic acid content of corn can cause the following side effects (11), (12):
Inflammation Stomach cramps Constipation Acute dermatitis or skin allergy (if you are allergic to grass) Bloating and gas Intestinal blockage Hemorrhoids Sudden weight gain
There is also a common misconception that you should avoid consuming corn to prevent diverticulitis (infection in the digestive tract). However, the actual side effects of corn are more related to digestive discomfort rather than directly causing such infections. Let us look at some data in the next section to find the truth.
Is Corn Bad For Diverticulitis?
In the past, individuals with diverticulitis were often advised to avoid nuts, corn, popcorn, and seeds to lower the risk of diverticular disease. However, there is limited evidence to support this advice. A study published in the Journal of American Medical Association that followed 47,228 men from 1986 to 2004 found that consuming nuts and popcorn was, in fact, linked to a reduced risk of the development of diverticular disease over an 18-year period. Therefore, individuals with known diverticula can safely consume nuts, corn, grains, and popcorn without increasing the risk of diverticulitis (13). Is corn better than rice? Corn contains more protein and fiber than rice and is considered a healthier option than rice (15), (16). Is corn high in sugar? Yes. Corn is high in natural sugars. One ear of fresh corn (102 g) contains 6.38 g of sugar (16). Hence, it is recommended to consume it in moderation. How much corn should I eat in a day? A 1-cup serving of corn is considered healthy to eat a day.
Illustration: Health Benefits Of Corn And Its Nutritional Facts
Discover 10 amazing benefits of corn for your health and nutrition! Watch this video to learn how this versatile food can help you stay healthy and fit.