What Is Jaggery?
Jaggery is made from the juice of sugarcane, which is heated to produce thick crystals. It contains sugar in sucrose form and is used in many food products as a sweetening agent. It is unrefined sugar, considered healthier than refined sugar as certain plant phytochemicalsi Substances present in plants that give their distinctive color, aroma, and flavor and help form resistance against plant virus infections, fungi, and other insects. and minerals are preserved in it (1). What Are Its Benefits? It aids in digestion and weight loss, slows down skin aging, cleanses the body, and reduces blood pressure. Who Can Consume It? Anybody can consume it except people with diabetes. How Often? You can consume 10 grams of jaggery daily. Caution Excess consumption can cause diarrhea and indigestion and increase the risk of intestinal infections.
Many people avoid jaggery as its raw appearance is not very appealing, but is jaggery good for health? And if so, how much jaggery is okay to eat everyday? It may be time to start making this food a regular part of your diet as it provides many essential nutrients and is an effective remedy for many ailments. As per Ayurvedic texts, jaggery has been used traditionally in various cultures as a natural remedy and functional food. Read on to learn more.
Traditional Uses Of Jaggery
Jaggery is widely valued across Latin America, Africa, and Southeast Asia for its natural sweetness, energizing qualities, and health benefits. In Latin America, it is known as ‘panela’ and used in drinks like ‘aguapanela’ for energy and as a remedy for colds. In Africa, jaggery is added to teas and porridges to soothe sore throats and combat fatigue. In Southeast Asia, jaggery enhances dishes, desserts, and drinks. Some communities also use it believing it is effective against digestive issues and for body cleansing. In India, it is commonly added to snacks like chikki (a peanut bar) mainly because of its binding properties when heated. Ayurvedic texts describe jaggery’s benefits for blood purification, digestive health, and even relief from bile disorders. It is also believed to stimulate digestion and appetite, which is why many recommend eating jaggery after a meal. Jaggery is known to ease respiratory issues and migraine. In fact, Jaggery’s ability to help with smoke-induced lung damage and reduce arsenic toxicity makes it a natural choice for protection against pollution (2). It has been trusted for generations, especially in rural communities as a daily health aid to support overall well-being. By adding jaggery to your diet, you gain a wide range of health benefits that you may not have thought it could provide. Let’s find out more about it! Jaggery is also known as ‘Gur’ in Hindi, ‘Bellam’ in Telugu, ‘Vellam’ in Tamil, ‘Sharkara’ in Malayalam, ‘Bella’ in Kannada, and ‘Gul’ in Marathi. Let’s take a look at all the amazing benefits of jaggery:
Skin Benefits Of Jaggery
Jaggery is also beneficial as a beauty treatment. It has natural properties that ensure that the skin stays healthy at all times.
Health Benefits Of Jaggery
For Digestion
One of the main reasons that people take jaggery after meals are due to its positive effects on the digestive system (2).
For Blood
Jaggery is known to have beneficial effects on the blood as well. This is why making it a part of your diet is recommended (2).
Jaggery Benefits For Weight Loss
Jaggery is surprisingly effective as an aid for weight loss. If you are looking to lose some unwanted pounds, include this food in your diet (4).
Other Benefits
Jaggery has many other benefits that include the following:
Jaggery Vs. Sugar: A Comparative Study
Let’s have a look at how jaggery is different from sugar.
1. Method Of Processing
Both jaggery and sugar are prepared by bringing sugar cane juice to a boil. However, this is only the initial step. The boiled juice is clarified with bone charcoal into a clear and transparent syrup which, upon cooling, condensation, and crystallization, turns into regular white sugar. On the other hand, sugar cane juice is boiled continuously in order to form a thick, sticky paste of jaggery. It is then cooled down and poured into molds to come up with required jaggery blocks (2), (3).
2. Composition
Sucrose (C12H22O12), a disaccharide (Glucose + Fructose), is known to be the primary component of both sugar and jaggery. While there is no other component in table sugar, jaggery is made of sucrose (65-85%), invert sugar (10-15)%, ash (2.5%), non-sugars such as calcium (0.4%), phosphorus, and very small amounts of dietary fiber, iron, and mineral salts. The invert sugar content of jaggery makes it higher in sweetness than regular sugar (3) and can also help balance out a low glycemic index.
3. Color
Regular sugar is white in color. But the color of jaggery can vary from golden yellow to different shades of brown (i.e. golden brown, perfect brown, dark brown, etc.). The color usually depends on the time of boiling the sugar cane juice (2), (3).
4. Texture
As far as the texture is concerned, sugar and jaggery are different from each other. Sugar has a solid and hard form that looks like crystal, while jaggery is semi-solid (comparatively softer) and does not have any specific shape (amorphous) (2), (3).
Recipes To Include Jaggery In Food To Curb Iron Deficiency
Jaggery is important for its iron benefits, and if you don’t like eating it raw, you can try the following methods. These are simple recipes you can make:
1. Jaggery Chapati
Grated jaggery Milk Wheat flour/Atta Salt to taste Ghee
This is one of the simplest ways to yield the benefits of jaggery.
2. Jaggery Rice
Jaggery Water Soaked rice Cloves Green cardamoms
It is done. Now you can savor and enjoy the food!
Prevent Iron Deficiency With Jaggery
Jaggery is a substitute for refined white sugar and is used in many Indian households. It is an excellent source of iron, and hence it helps prevent iron deficiency and improves the hemoglobin levels in the blood (2): If you do not eat green vegetables daily, then you can eat jaggery on a daily basis to fulfill the iron requirements of your body.
You can add jaggery to substitute for sugar in your tea or coffee.
You can add it to your breakfast cereal, sambhar, rasam, and dal.
You can replace refined white sugar with jaggery while preparing some Indian sweets such as kheer or payasam.
Is consuming jaggery for diabetes considered safe? Well, jaggery should be consumed with caution if you are diabetic as it contains only five percent fewer carbohydrates when compared to white sugar. It can increase your sugar levels drastically. So, if you are a diabetic or on a weight loss program, you should not consume it in large quantities. Also, it may cause some side effects if consumed in excess amounts. Scroll down to know in detail about those adverse reactions.
Side Effects Of Jaggery
Some potential adverse effects of jaggery are as follows:
May Cause Digestive Issues: The excess intake of jaggery may cause stomach pain, gas, bloating, and diarrhea in some people with sensitive stomachs. However, limited data is available to prove these claims. May Lead To Tooth Decay: Anecdotal evidence suggests that just like other sugary items, jaggery may also lead to dental issues like tooth decay and cavities. May Cause Weight Gain: The high calorific value of jaggery may contribute to weight gain when it is consumed in excess amounts. However, limited data is available in this regard. May Cause Allergic Reactions: It may cause itching, swelling, and breathing issues in some individuals. If you are intolerant to sugar, it is advised to avoid jaggery consumption.
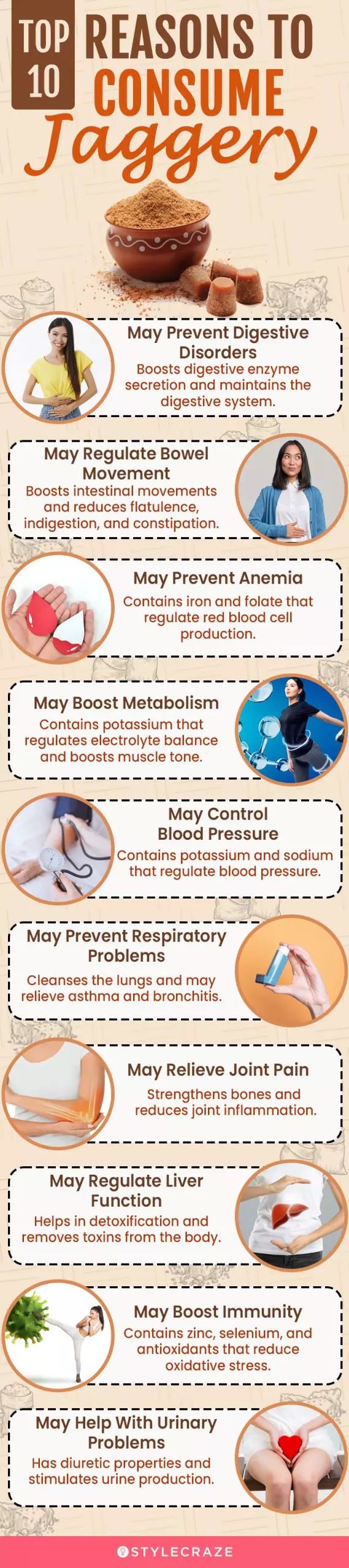
Therefore, certain groups should be cautious about consuming jaggery. For example, people with sensitive stomachs, those prone to dental issues, individuals managing their weight, and people with sugar intolerance or allergies. How much jaggery is okay to eat every day? Check out the infographic below to learn more about the top reasons to substitute your regular white sugar with the wonderous jaggery.Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team Generally, ten grams of jaggery is safe for daily consumption. Consult a doctor regarding consumption in case you have a specific condition. Does jaggery increase belly fat? Although jaggery may not particularly increase belly fat, consuming it in excess daily may lead to weight gain due to its high glucose and fructose content. Hence, moderate consumption is advised. Is jaggery better than honey? Both jaggery and honey have their own benefits. Jaggery is rich in copper, magnesium, and iron, whereas honey is rich in vitamins B and C and iron. Hence, what you choose depends on your preferences and health conditions.
Illustration: Marvelous Benefits Of Jaggery For Skin And Health
Unveil the sweet truth about jaggery in this enlightening video. Explore why this golden alternative surpasses regular sugar, uncovering its multitude of health benefits that can revolutionize your well-being.









![]()

